Back to: Software Development (VCE Units 3 & 4)
The problem-solving methodology comprises the four stages of: analysis, design, development and evaluation. For each of these stages there is a typical set of activities, as shown in the figure below. Specific details of the scope of the problem-solving methodology stages are provided in the Problem-solving methodology specifications and the introduction to the relevant areas of study. Note: when creating solutions, this methodology can be applied as a single stage-by-stage problem-solving process or applied to each iteration of an agile problem-solving process.
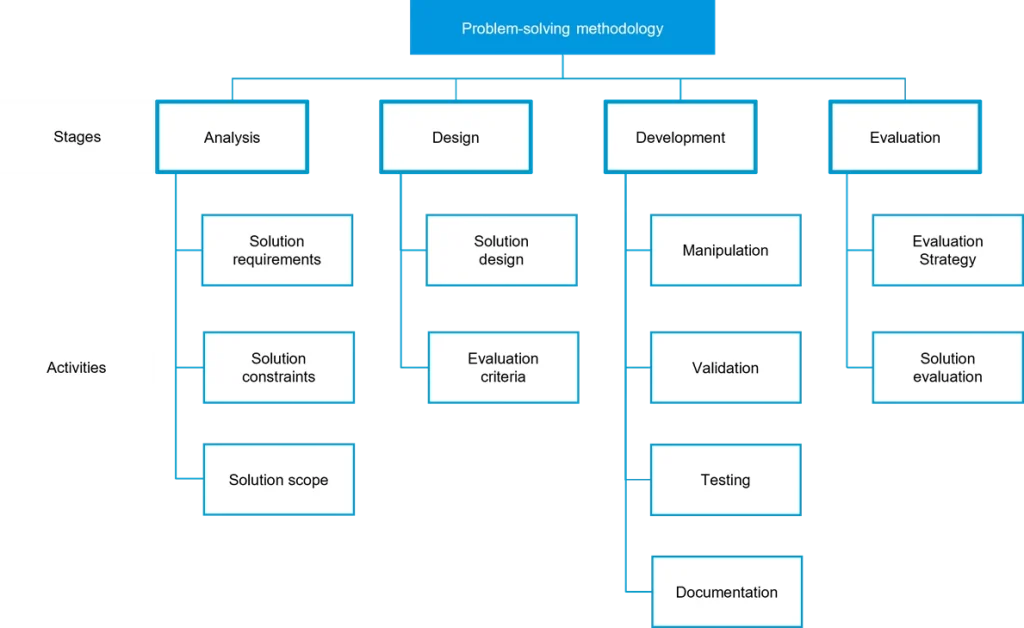
Analysis
Involves determining what is required to solve a problem. This involves acquiring and analysing data, and then identifying the solution requirements, constraints and scope
Solution requirements
Solution requirements can be described as functional and non-functional.
- Determine the functional requirements of the solution. These describe what the software solution should do. This involves specific details such as input required, output developed and functions of the solution, including data manipulation and validation.
- Determine the non-functional requirements. These describe the quality attributes of the solution, including usability, reliability, portability, robustness and maintainability.
- Use tools to assist in determining solution requirements, including context diagrams, data flow diagrams and use case diagrams.
Solution constraints
Solution constraints can be described as the conditions or limitations that must be considered when designing a solution.
- Determine the constraints of the solution. These include economic (cost and time), technical (speed of processing, capacity, availability of equipment, compatibility, security), social (level of expertise of users), legal (intellectual property, ownership of data, privacy of data), and usability (accessibility, usefulness, ease of use).
Solution scope
Solution scope describes the boundaries or parameters of the solution.
- Identify what will be and/or what will not be addressed by the solution.
Skills you’ll use for the Analysis stage
- Collect data using a range of techniques to determine and clarify user needs, solution requirements, constraints and scope.
- Collect primary and secondary data and prepare data for identifying trends, patterns and relationships.
- Critically analyse the sources of data and information to determine reliability, validity and relevance.
- Draft and evaluate questions to critically analyse requirements, problems, needs or opportunities.
- Develop strategies for asking follow-up questions to further clarify the data and information collected.
Design
involves determining how the solution requirements will function and appear. It involves designing the functionality, appearance and user interface of the solution and developing evaluation criteria to determine the efficiency and effectiveness of the software solutions.
Solution design
Solution design focuses on the development of design ideas into preferred designs using design principles and a range of relevant design tools.
- Design how the solution will function and appear by identifying the specific data required and how it will be named, structured, validated and manipulated.
- Use ideation techniques and tools for generating design ideas, including mood boards, brainstorming, mind maps, sketches and annotations.
- Use design tools to demonstrate structure and functionality, including data dictionaries, input–process–output (IPO) charts, object descriptions, flowcharts and pseudocode.
- Use design tools to show the relationships between the components of a solution, including annotated diagrams, mock-ups, storyboards, sitemaps, queries, context diagrams, data flow diagrams and use case diagrams.
- Use design tools to design the visual components of a solution (user interface, graphic representations or data visualisations), including layout diagrams, annotated diagrams and mock-ups. This includes identifying the position and size of text, images and graphics, font types and styles, colours and text enhancements.
Evaluation criteria
Evaluation criteria measure the efficiency and effectiveness of designs and the entire solution.
- Develop evaluation criteria to determine the degree to which solution designs meet requirements.
Note that the same evaluation criteria are used in the Evaluation stage to determine the degree to which the solution meets requirements. In the Evaluation stage, the evaluation criteria measure the efficiency and effectiveness of the solution. - Modify and refine the evaluation criteria as the solution develops.
Development
involves transforming the requirements and designs into a working software solution. It involves the manipulation and validation of data, testing to ensure the software solution meets requirements and generating documentation to support the use of the solution.
Manipulation
Manipulation involves applying a range of functions and techniques using software tools (coding).
- Develop the solution to meet specifications using appropriate algorithms, features of programming languages or software functions and techniques.
- Apply appropriate formats and conventions to enhance the appearance of solutions.
- Perform calculations using descriptive statistics and identify trends, patterns and relationships.
Validation
Validation checks the reasonableness of data being input. Validation can be both manual and electronic.
- Use validation techniques to check data entry for reasonableness and completeness of data, including existence check, range check and type check.
- Use verification techniques after data entry to ensure that data entered matches the source data, including proofreading, confirming the data against other sources and checking that the data visualised is consistent with the data acquired/collected.
- Note that the effectiveness of validation is determined through the testing activity below.
Testing
Testing checks whether solutions meet all the requirements, function as expected and are usable by intended users.
- Conduct debugging techniques to ensure solutions meet requirements.
- Develop a testing strategy to ensure that the solution works as intended, including features to be tested, test data and expected results.
- Conduct tests, record the actual results and compare the actual results of the tests against the expected results.
- Correct identified errors.
Documentation
Documentation is used to explain the structure and behaviour of a solution.
- Write internal documentation to support the functioning, maintenance and upgrading of the solution.
- Modify and evolve designs as the solution develops.
- Modify and refine the evaluation criteria as the solution develops.
Evaluation
Involves determining the degree to which the software solution has met requirements. It involves developing a strategy to evaluate the software solution after implementation and evaluating the software solution against the evaluation criteria to see how well it meets requirements.
Evaluation strategy
Evaluation strategies focus on how the solution will be evaluated, including evaluation criteria, time frame and responsibility.
- Propose a strategy to evaluate the extent to which the solution meets identified problems, needs or opportunities, or solves the identified problem after the solution has been developed and implemented.
- Specify a timeline for evaluation, the data to be collected, methods and techniques for data collection, who is responsible for collection and how the data relates to the evaluation criteria.
Solution evaluation
Solution evaluation determines whether a solution has met requirements.
- Use the evaluation criteria to determine how the solution has met requirements, needs or opportunities. Discuss in terms of efficiency and effectiveness of the solution.
Skills underpinning the Evaluation stage
- Critically evaluate the analysis process and discuss how it assisted in meeting the requirements, problems, needs or opportunities.
- Critically evaluate the design process and discuss how it assisted in meeting the requirements, needs or opportunities.
- Identify and discuss any improvements that could be made to the solution by approaching the problem-solving methodology process differently.
